HYPERPIGMENTATION TREATMENT IN TOLEDO
WHAT IS HYPERPIGMENTATION?
TYPES OF HYPERPIGMENTATION
Melasma. Melasma is believed to be caused by hormonal changes and may develop during pregnancy. Areas of hyperpigmentation can appear on any area of the body, but they appear most commonly on the stomach and face.
Sunspots. Also called liver spots or solar lentigines, sunspots are common. They’re related to excess sun exposure over time. Generally, they appear as spots on areas exposed to the sun, like the hands and face.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. This is a result of injury or inflammation to the skin. A common cause of this type is acne.
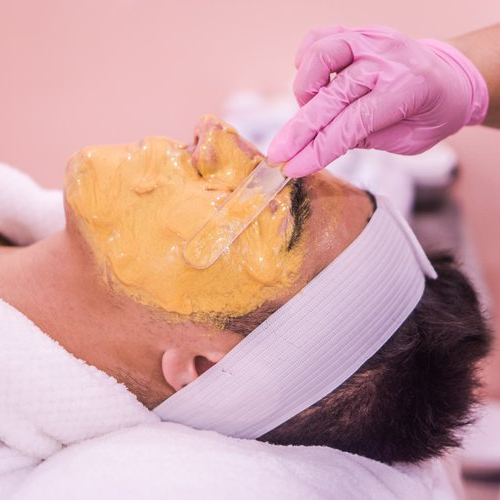
WHAT PRODUCTS TREAT HYPERPIGMENTATION?
Brightening ingredients, SPF
Jan Marini Bioglycolic Cleanser, CESTA Face Serum, Luminate Face Lotion, Marini Physical SPF
Circadia Amandola Milk Cleanser, Vitamin C Reversal Serum, Licorice & Bearberry Brightening Mist, Light Day Sunscreen
WHAT TREATMENTS TARGET PIGMENTATION?
1 .CHEMICAL PEELS
2. HYDRAFACIAL BRITENOL BOOSTER
Did You Know?
Our expert estheticians offer a wide range of services, including facials, microdermabrasion, chemical peels, and more, tailored to meet your unique skincare needs.
Conveniently located, we proudly serve clients throughout Northwest Ohio and Southeast Michigan, bringing the glow of healthy, radiant skin to our entire community. Experience the difference of our luxurious spa atmosphere and unparalleled commitment to your skincare journey. Book your appointment today and discover a more confident, beautiful you.
Areas Served
-
Bedford, Michigan
-
Bowling Green, Ohio
-
Elmore, Ohio
-
Genoa, Ohio
-
Haskins, Ohio
-
Holland, Ohio
-
Luckey, Ohio
-
Luna Pier, Michigan
-
Maumee, Ohio
-
Monclova, Ohio
-
Monroe, Michigan
-
Northwood, Ohio
-
Oregon, Ohio
-
Ottawa Hills, Ohio
-
Ottawa Lake, Michigan
-
Perrysburg, Ohio
-
Point Place, Ohio
-
Rossford, Ohio
-
Samaria, Michigan
-
Swanton, Ohio
-
Sylvania, Ohio
-
Temperance, Michigan
-
Toledo, Ohio
-
Walbridge, Ohio
-
Woodville, Ohio
Additional Services
